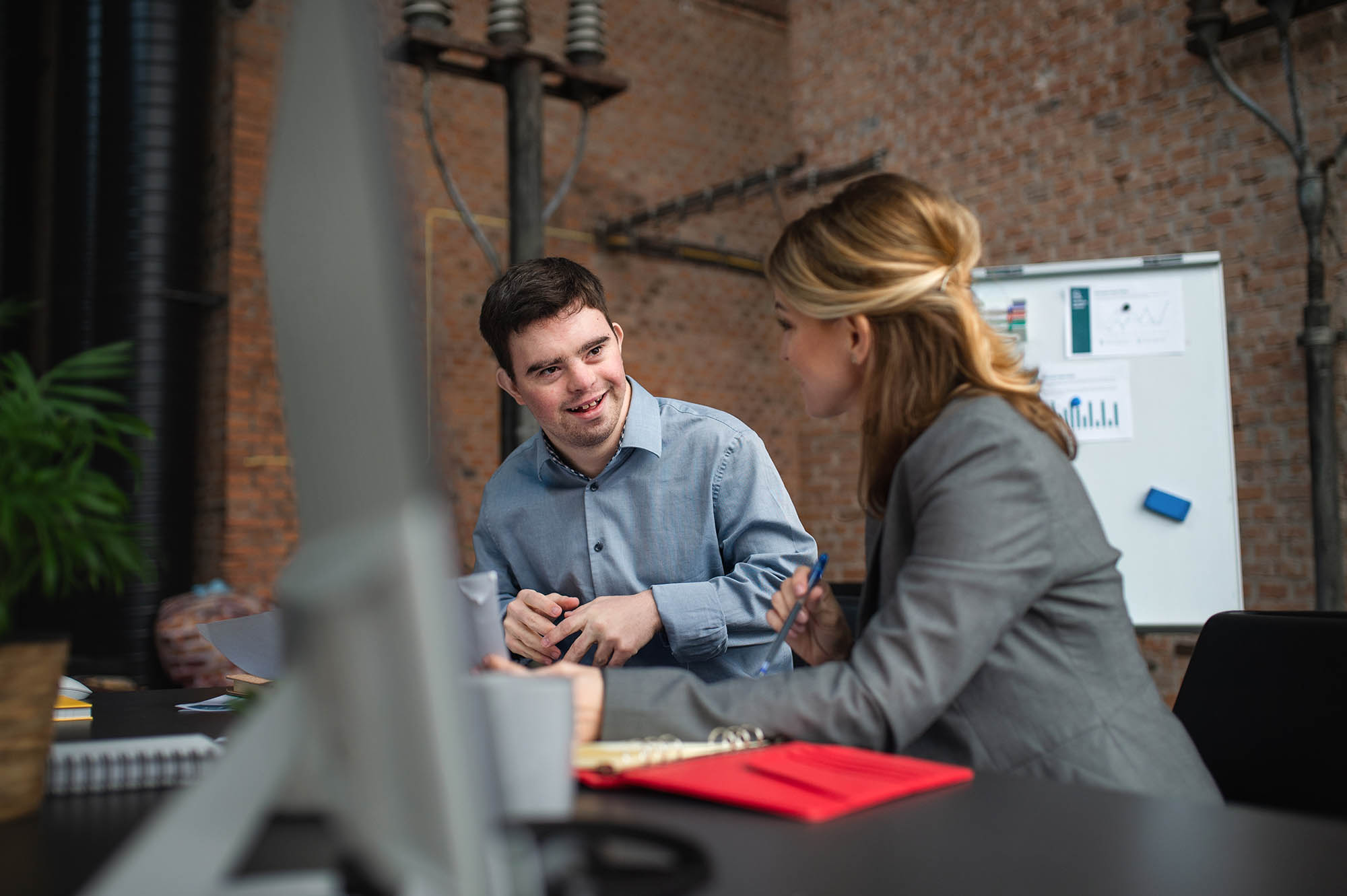
What is Postsecondary Transition for Students with Disabilities?
Postsecondary transition planning for students with disabilities is a process beginning at age 14 (or earlier if appropriate) designed to help students reach their vision for a meaningful and productive future as they transition into adulthood.
Postsecondary transition for students with disabilities is a student-centered process that includes ongoing assessment, services, instruction, experiences, opportunities, and supports designed to elevate students’ in-school and post school outcomes.
Why Is It Important?
”Contemporary transition policies and practices are grounded in the belief that students with disabilities are far more likely to achieve their aspirations for life after high school if provided the right combination of opportunities, instruction, services, and support [in high school]. This belief aligns with the special education’s overarching purpose to “prepare students with disabilities for further education, employment, and independent living” to ensure “equality of opportunity, full participation, independent living, and economic self-sufficiency (IDEA. 2004)”.
(Trainor et. al., 2019) (Division of Career Development & Transition)
Our process
Postsecondary Transition Services Flow Chart
The Postsecondary Transition Services Flow Chart provides a concise, visual overview of the process from age‑appropriate assessments and goal setting to coordinated transition services and positive post‑school outcomes. By mapping each stage—from identifying strengths and needs to collaborating with outside agencies—this chart ensures educators, families, and community partners can clearly see how to guide students toward meaningful adult life.
Center for Change in Transition Services, Seattle University, Seattle, WA
Key Questions About Postsecondary Transition Planning
This FAQ covers key elements of postsecondary transition planning—how students participate in their IEP, definitions of assessments, goals, services, courses of study, and annual IEP objectives. It helps families, educators, and community partners create a cohesive plan that supports students’ success beyond high school.
Student Participation in Postsecondary Transition IEP
Beginning at age 14, students must be invited to postsecondary transition IEP planning meetings. Student-driven IEPs increase self-advocacy skills, disability awareness, and create a rich and meaningful postsecondary transition IEP for the student. When students are involved in their postsecondary transition planning, they are more motivated to engage in the opportunities, instruction, services and supports outlined in the postsecondary transition plan.
Postsecondary Transition Assessment Definition
“Postsecondary transition assessment for students with disabilities is “the ongoing process of collecting data on the individual’s strengths, needs, preferences, and interests as they relate to the demands of current and future working, educational, living, and personal, and social environments. Assessment data serve as the common thread in the postsecondary transition process for students with disabilities and form the basis for defining goals and services to be included in the IEP” (Sitlington, 1996). (Division of Career Development & Transition)
Measurable Postsecondary Goals(PSGs) Definition
PSGs are goals for the future that are written as the target for after high school and state what the student will do in the areas of employment, further education, and independent living. They are goals that are based on the results of postsecondary transition assessments and include the interests and vision of the student. These goals are likely to narrow in focus and become more refined as the student gets older.
Postsecondary Transition Services Definition
Postsecondary Transition services are a coordinated set of activities, including instruction, experiences, strategies, steps, or actions, provided by the community of adults that support the student’s progress toward achieving their post-secondary goals (PSGs). Postsecondary transition services should be designed to address all areas the student may need to facilitate their transition to post school life. Analyzing the gaps in skills of the student is important for designing appropriate postsecondary transition services to achieve the PSGs.
Courses of Study Definition
When developing the postsecondary transition plan, careful consideration must be given to the courses of study for the student. The courses of study must be individualized and based on the needs of the student and specifically aligned to the goals and services outlined in the postsecondary transition plan. The courses of study is a multi-year description of coursework that is specific and considers the student’s preferences and interests and that will reasonably enable the student to reach their postsecondary goals.
Annual IEP Goals Related to Postsecondary Transition Services
Developing annual postsecondary transition IEP goals will help the student work on areas of skills needed and measure progress towards achieving their postsecondary goals (PSGs). The annual IEP goal(s) must be individualized and based on the specific student needs. These goals are written in the same part of the IEP that includes all the other annual IEP goals.
Coordinating with Other Agencies
Connecting students and families with other agencies that serve adults with disabilities helps “create a bridge” between high school and adult life, allowing the student to build community relationships and supports before leaving high school.
Pre-Employment Transition Services (Pre-ETS)
Pre-Employment Transition Services (Pre‑ETS) equip students with disabilities with skills and training to explore careers, develop workplace readiness, and secure competitive employment.

Job Exploration Counseling
Discussion or counseling of job exploring options intended to foster motivation, consideration of opportunities and informed decision-making.
Work-Based Learning Experiences
An educational approach that uses the workplace or real work to provide students with the knowledge and skills that will help them connect school experiences to real-life work activities and future career opportunities. These opportunities are meant to engage, motivate and augment the learning process.
Counseling on Post Secondary
Students gain an awareness of the wide range of career pathway options and labor market realities and projections. Students explore how skill development and knowledge relate to future opportunities in postsecondary Education (PSE) settings and employment.

Workplace Readiness
Workplace Readiness skills encompass the abilities that help employees learn how to interact with supervisors and co-workers. They help reinforce the importance of timeliness and build an understanding of how we are perceived by others.
Instruction in Self Advocacy
Self-advocacy includes instruction regarding an individual’s ability to effectively communicate, convey, negotiate or assert his/her own interests and/or desires. Emphasis is on taking responsibility for communicating one’s needs and desires in a straightforward manner to others.
Additional Resources
Explore essential documents and tools that provide insights into effective transition planning and support post-school success.
Portrait of Postsecondary Transition (Coming Soon!)

